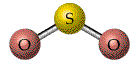Shapes of Molecules and VSEPR Theory
Dr. Walt Volland revised April 2004|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
After you have studied this lesson you should be able to:
|
||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
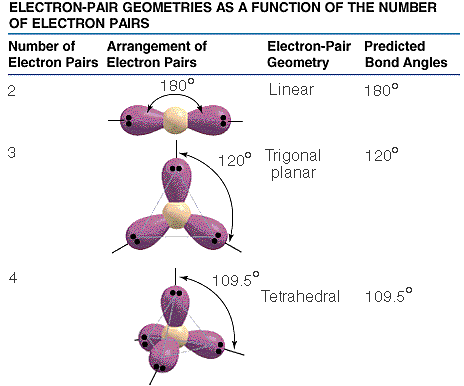
The valence shell electron-pair repulsion model, VSEPR, model attempts to predict molecular shapes. The model assumes that electron pairs around a central atom repel one another. Repulsions between the electron pairs force definite positions based on the number of "groups" or electron clouds. The model deals with counting groups of electrons radiating out from a "central atom" . The model is can make accurate predictions. We will deal only with central atoms that have from two, three or four groups of electrons radiating from the central atom. The process of determining the structure uses the following steps.
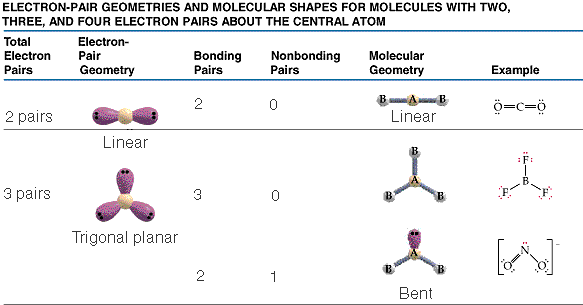
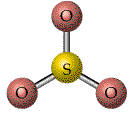
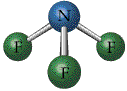
The three types of basic structures are shown here.NOTE the electron pairs are also equivalent to "groups" of electrons such as lone pairs, double bonds and triple bonds. The central atoms shown here are the building blocks for huge molecules. The angles and shapes in DNA can be predicted using the same VSEPR style model.
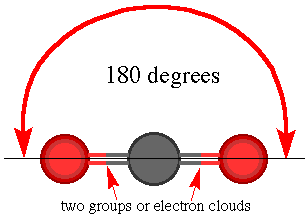
The
shape for BeCl2 is the same because there are two groups
of electrons around the Be atom.
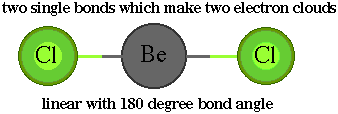
Examples of molecules and shapes
|
||||||||